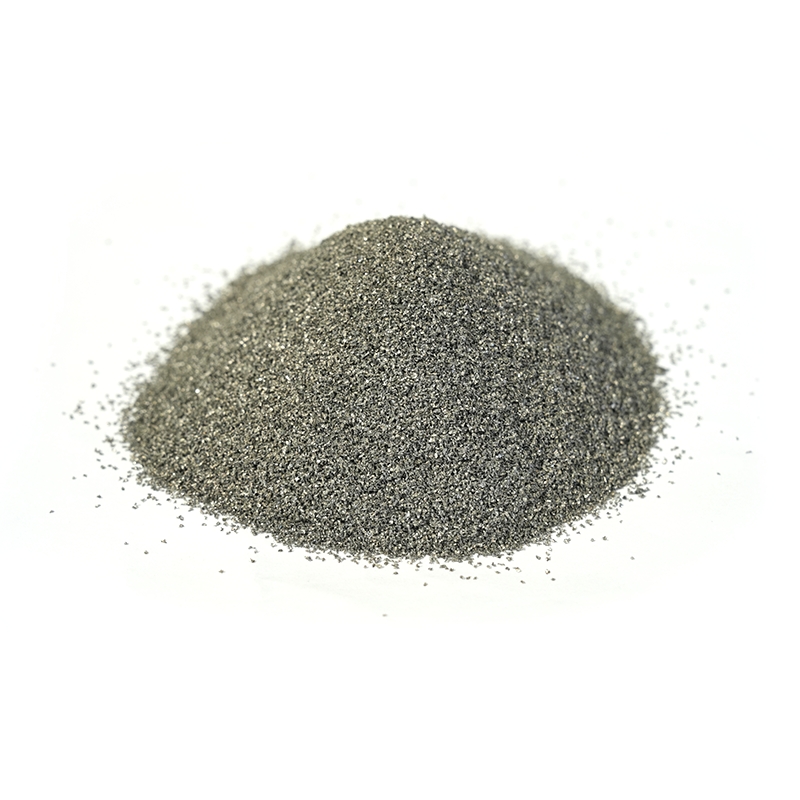
Alloy powder, also known as metal powder or powdered alloy, plays a critical role in modern industrial manufacturing. As a finely ground mixture of two or more metals—or metals combined with non-metals—alloy powder has become a fundamental material in various high-tech applications. From automotive components and aerospace structures to 3D printing and electronics, the use of metallic powder has revolutionized production processes.
What Is Alloy Powder?
Alloy powder refers to a blend of metallic elements that are mechanically or chemically combined in powder form. These metal powders are produced through methods such as atomization, mechanical alloying, or reduction. The resulting powdered alloys retain the beneficial properties of their base metals, such as strength, corrosion resistance, conductivity, and heat tolerance.
Common alloy powders include stainless steel powder, copper alloy powder, nickel-based powder, titanium alloy powder, and aluminum alloy powder. Each type of metallic powder serves specific functions depending on the composition and desired performance.
Production Techniques for Alloy Powder
There are several manufacturing techniques used to produce alloy powders:
Gas Atomization – A widely used method where molten metal is sprayed into fine droplets and solidifies into powder.
Water Atomization – A cost-effective method producing irregular-shaped metal powders ideal for pressing and sintering.
Mechanical Alloying – This process blends pure metal powders through repeated welding, fracturing, and re-welding in a high-energy ball mill.
Electrolysis and Reduction – Suitable for producing high-purity powdered alloys with specific compositions.
Each production method affects the particle size, shape, and properties of the alloy powder, which in turn impacts the final product’s performance.

Applications of Alloy Powder
The growing demand for metal powder materials across multiple industries reflects their versatility and performance. Here are key application areas:
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Alloy powders are essential in powder-bed fusion and direct energy deposition processes, enabling the fabrication of complex, high-precision metal parts.
Powder Metallurgy: In this process, powdered alloy is compressed into desired shapes and then sintered to form solid metal components. It is widely used in automotive and machinery manufacturing.
Thermal Spraying: Metallic powder is applied to surfaces to improve wear resistance, thermal insulation, or corrosion protection.
Electronics and Semiconductors: Fine metal powders are used in conductive inks, contacts, and solder materials.
Advantages of Using Alloy Powder
The use of alloy powder in industrial applications offers several key benefits:
Material Efficiency: Minimizes waste compared to traditional subtractive machining.
Customization: Allows for precise tailoring of material properties.
Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces processing steps and energy consumption.
Enhanced Performance: Offers improved strength-to-weight ratio, conductivity, and resistance to environmental damage.
Future Trends in Alloy Powder
With advancements in nanotechnology and metallurgy, the scope of metal powder applications continues to grow. Researchers are developing nano-scale powdered alloys with superior mechanical and thermal properties for use in biomedical implants, energy systems, and next-generation electronics.
Moreover, the ongoing rise of sustainable manufacturing is driving the adoption of recyclable and environmentally friendly metallic powder materials, making alloy powder a cornerstone of green production technologies.


 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى