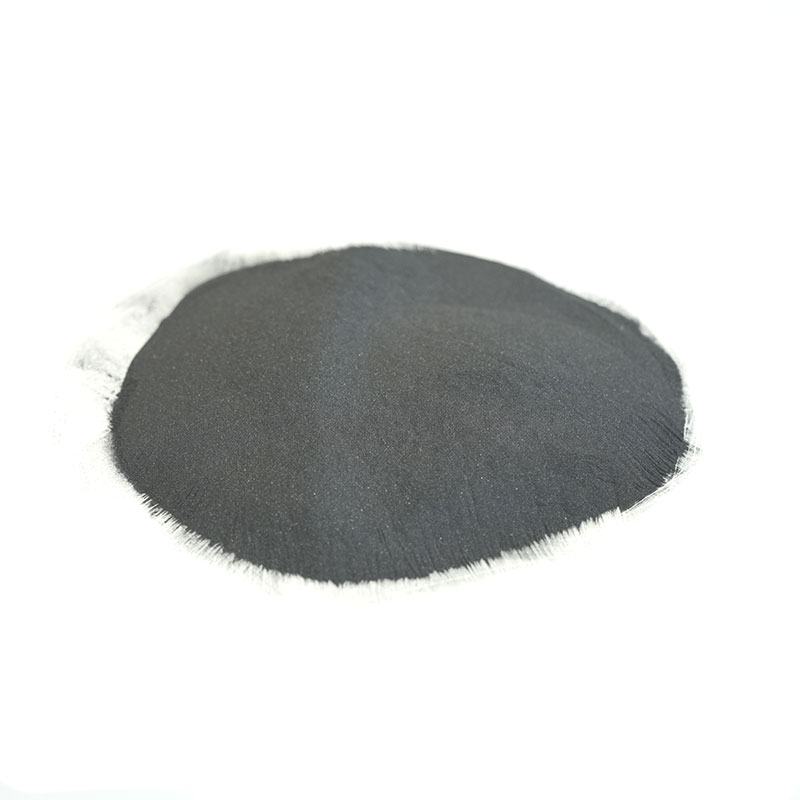
Carbide powders are a family of materials, but when people typically refer to "carbide powder" in an industrial context, they are most often talking about tungsten carbide (WC). However, other important carbides include silicon carbide (SiC), titanium carbide (TiC), chromium carbide (CrC), boron carbide (B4C), and even more exotic ones like tantalum carbide (TaC) or hafnium carbide (HfC).
The defining characteristic of these materials is their extreme hardness, high melting points, and excellent wear resistance, which stems from the strong covalent and ionic bonds within their crystal structures. These properties make them invaluable in a diverse range of high-performance applications.
Let's elaborate on the key uses:
-
Cutting Tools and Machining (The Dominant Application): This is by far the most significant use of tungsten carbide powder. WC powder is typically mixed with a binder metal, most commonly cobalt (Co), and then compacted and sintered at high temperatures to form a composite material known as cemented carbide or hardmetal. The cobalt acts as a binder, holding the hard WC grains together and providing toughness.
- Turning, Milling, Drilling Inserts: These are the replaceable cutting tips used in lathes, milling machines, and drills to shape metals. They are crucial for machining hard and abrasive materials like steel, cast iron, stainless steel, and superalloys, which would quickly wear out conventional high-speed steel tools.
- Solid Carbide Tools: Drills, end mills, reamers, and burrs made entirely of cemented carbide offer superior rigidity and tool life for precise machining operations.
- Saws and Routers: Used in woodworking, metalworking, and for cutting composites.
- Mining and Construction Tools: Drill bits for rock drilling, road milling inserts, tunnel boring machine cutters, and foundation drilling tools all rely on the extreme toughness and wear resistance of cemented carbides to break through hard rock and abrasive soil.
-
Wear Parts: Beyond cutting, carbide's wear resistance makes it ideal for components subjected to high friction, abrasion, erosion, or impact.
- Nozzles: For abrasive blasting, waterjet cutting, and spray applications where conventional metals would quickly wear away.
- Pumps and Valves: Liners, impellers, and seals in pumps handling abrasive slurries or corrosive fluids.
- Dies and Punches: For stamping, drawing, and forming operations where high wear resistance is needed to maintain part precision over long production runs.
- Bearings and Seals: In highly demanding environments where lubrication might be limited or temperatures are extreme.
- Grinding Media: Balls or cylinders used in mills for grinding hard materials.
-
Thermal Spray Coatings (Hardfacing): Carbide powders are frequently used to create protective coatings on the surfaces of components. Techniques like High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) spraying, plasma spraying, or even laser cladding are used to deposit a layer of carbide (often WC-Co, CrC, or mixtures) onto a substrate.
- Extending Component Life: These coatings significantly enhance wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and sometimes even heat resistance for parts in industries like aerospace (landing gear, engine components), oil & gas (drilling tools, valve seats), and general manufacturing.
- Repair and Reclamation: Worn parts can be refurbished by applying new carbide coatings.
-
Abrasives: Due to their hardness, some carbides, especially silicon carbide (SiC) and boron carbide (B4C), are excellent abrasives.
- Grinding Wheels and Discs: Used for grinding and cutting extremely hard materials.
- Sandpaper and Abrasive Belts: SiC is a common abrasive grain.
- Lapping and Polishing Compounds: Fine carbide powders are used to achieve very smooth and precise finishes on hard surfaces.
-
Armor and Ballistics: Boron carbide (B4C) and, to a lesser extent, silicon carbide, are among the hardest man-made materials and are used in lightweight ceramic armor applications.
- Body Armor: Ceramic plates in bulletproof vests and tactical gear.
- Vehicle Armor: For military vehicles and aircraft.
-
High-Temperature and Specialty Applications:
- High-Temperature Furnaces: Some carbides (e.g., SiC) are used for furnace elements, refractories, and crucibles due to their stability at extreme temperatures.
- Nuclear Applications: Boron carbide (B4C) is an excellent neutron absorber, making it valuable for control rods and shielding in nuclear reactors.
- Aerospace: Tantalum carbide (TaC) and Hafnium carbide (HfC) are ultra-high-temperature ceramics with potential for use in hypersonic vehicle components and rocket nozzles due to their extreme melting points.
- Catalysts: Some carbides, particularly molybdenum carbide (Mo2C), are being researched as cost-effective alternatives to precious metal catalysts in various chemical reactions due to their similar electronic structures.
-
Consumer Products:
- Jewelry: Tungsten carbide has become very popular for rings and watches due to its exceptional scratch resistance and durability, making it much harder to scratch than gold or silver.
- Ballpoint Pen Tips: Small carbide balls are used for the tips of ballpoint pens due to their wear resistance and ability to transfer ink smoothly.
In summary, carbide powders are essential for any application requiring materials that can withstand extreme wear, abrasion, high temperatures, and high stresses. Their unique combination of properties has made them indispensable across heavy industry, manufacturing, defense, and even consumer goods.



 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى