Metal powders for filtration have become an essential material in modern industrial applications, offering superior performance, durability, and precision compared to traditional filter media. These powders are widely used in industries such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage production, water treatment, and gas purification. By utilizing the unique properties of metallic materials, filters made from metal powders provide reliable separation efficiency, long service life, and high-temperature resistance.
1. What Are Metal Powders for Filtration?
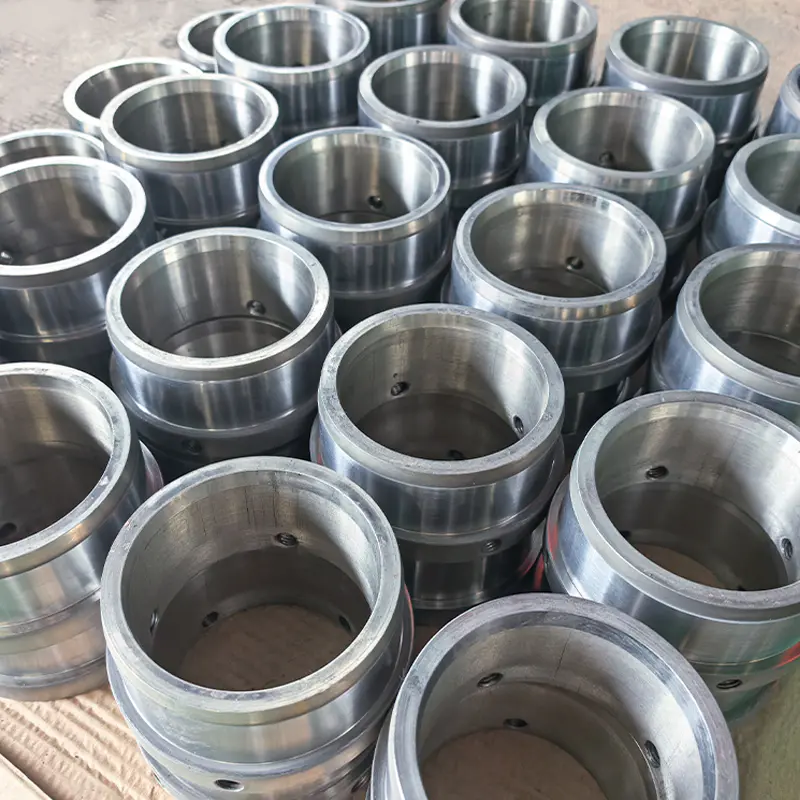
Metal powders for filtration refer to finely divided metallic particles, such as stainless steel, bronze, nickel, titanium, or other alloys, that are sintered to form porous filter elements. The sintering process fuses the powder particles together under controlled heat and pressure, creating a rigid and permeable structure. This structure allows gases or liquids to pass through while effectively trapping contaminants, particles, and impurities.
The key advantage of using metal powders for filtration lies in the ability to control pore size, porosity, and mechanical strength through precise powder selection and sintering parameters. This ensures that the final product meets the exact filtration requirements of various industrial processes.
2. Characteristics of Metal Powders for Filtration
High Filtration Efficiency: The uniform pore structure of sintered metal powder filters enables precise particle retention and consistent filtration performance.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance: Materials such as stainless steel and titanium offer excellent resistance to corrosion and chemical attack, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments.
High Temperature Tolerance: Metal filters can operate under extreme temperatures, far exceeding the limits of polymeric or fabric filters.
Mechanical Strength and Reusability: The rigid structure allows for backwashing, cleaning, and reuse without compromising filtration efficiency.
Customizable Pore Size: The particle size of the metal powder determines the pore size of the filter, allowing manufacturers to produce filters with a wide range of permeability levels.
3. Common Materials Used in Metal Powder Filters
Stainless Steel Powder: The most widely used material due to its balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and affordability.
Bronze Powder: Often used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems for its excellent self-lubricating and corrosion-resistant properties.
Nickel and Nickel Alloys: Provide superior resistance to oxidation and corrosion in high-temperature applications.
Titanium Powder: Known for its biocompatibility and excellent performance in medical, chemical, and seawater filtration systems.

4. Applications of Metal Powders for Filtration
Metal powders for filtration are used in diverse applications that demand both mechanical strength and precision filtering:
Chemical and Petrochemical Industry: For filtration of catalysts, acids, and process gases.
Pharmaceutical and Food Processing: For sterile filtration and purification of liquids.
Water and Wastewater Treatment: For filtering suspended solids and ensuring water purity.
Automotive and Aerospace: For hydraulic systems, fuel filtration, and exhaust gas purification.
Medical Devices: In biomedical applications where sterility and corrosion resistance are crucial.
5. Advantages Over Conventional Filter Media
Compared with fabric, paper, or polymer filters, metal powders for filtration offer longer life cycles, superior cleaning ability, and stable performance under extreme conditions. They can be regenerated through ultrasonic cleaning or reverse flow, reducing maintenance costs and waste generation. Additionally, metal filters can be fabricated in various shapes—cylindrical, disc, or conical—to fit specific equipment designs.
6. Future Development and Innovation
With ongoing advancements in powder metallurgy and material science, metal powders for filtration continue to evolve. Innovations in alloy design, additive manufacturing, and nanostructured metal powders are enabling filters with even finer porosity, improved flow characteristics, and enhanced resistance to fouling. These developments are expected to expand the application scope of metal powder filters in green energy, environmental protection, and high-precision manufacturing.
Conclusion
Metal powders for filtration combine the strength of metal with the precision of engineered porosity, delivering a superior solution for modern industrial filtration needs. Their durability, reusability, and adaptability make them an increasingly preferred choice across multiple sectors. As industries move toward sustainability and higher efficiency, metal powders for filtration will continue to play a critical role in ensuring clean processes and reliable performance.


 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى